Commentary - Imaging in Medicine (2015) Volume 7, Issue 2
PSMA PET/CT imaging and therapy
levent kabasakal* & Emre Demirci
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Istanbul University, Turkey
- Corresponding Author:
- levent kabasakal
Department of Nuclear Medicine
Istanbul University, Turkey
Tel: +905323667908
E-mail: lkabasakal@tsnm.org
Abstract
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is increasingly recognized as a novel target for the PET imaging of prostate cancer (PCa) and 68Ga-DKFZ-11 (68Ga-PSMA) has been suggested as a novel tracer for detection of PCa relapses and metastasis. First human studies of PSMA PET/CT imaging have demonstrated high tracer uptake at the sites of primary tumor and lymph node and bone metastasis in direct correlation with aggressiveness and Gleason scores. PSMA PET/ CT seems to be a highly accurate imaging tool for restaging of prostate cancer patients with biochemical recurrence. PSMA PET/CT imaging may be used in order to develop a treatment strategy for recurrent disease even in patients with low PSA levels. As a theranostic approach its counterpart Lu-177 labelled ligands have a potential role for the treatment of castration resistant prostate cancer.
Keywords
Prostate cancer; PSMA; PET/CT; biochemical recurrence; choline
Prostate cancer (Pca) is the most common solid cancer in men and prostate cancer is the second most common cause of death in developed countries [1]. Radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are performed as primary therapy with a curative intent in patients with localized prostate cancer [2,3]. The selection of therapy in prostate cancer is mainly influenced by the presence or absence of metastasis. Studies with cross-sectional imaging with computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or functional imaging with F-18-FDG PET/CT and F-18-Choline PET/ CT have shown disappointing sensitivity rates in detecting lymph node positive disease [4,5]. Pelvic lymph node dissection is considered as the gold standard for evaluating the presence of nodal involvement in patients with risk of nodal metastasis [6]. Currently there is no reliable imaging method for detecting lymph node metastasis.
Despite effective definitive therapy depending on the patient population studied, 15% to 40% of patients experience increasing PSA levels, which is called biochemical recurrence. European Association of Urology guidelines define biochemical recurrence as an increase of serum PSA value above 0.2 ng/ml and over 2 ng/ ml above the nadir value after radiation therapy [2,3]. An accurate diagnosis of the site of prostate cancer recurrence is a key factor for treatment planning and patient management [3]. The selection of therapy in recurrent prostate cancer is mainly influenced by the presence or absence of metastasis, since salvage therapy is indicated in localized recurrent disease and systemic therapy is indicated in metastatic disease. Studies with morphological imaging with CT and MRI, or functional imaging with F-18-FDG PET/ CT and F-18-Choline PET/CT have shown disappointing sensitivity rates [7] and currently there is no reliable imaging method for detecting the site of disease in patients with biochemical recurrence [6-10]. Therefore, there is an absolute necessity for a diagnostic tool for precise localization of recurrences in asymptomatic patients with a rising prostate specific antigen (PSA) after definitive therapies, which could impact on management decisions [8-10].
Glutamate carboxypeptidase II, also known as prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is a zinc dependent peptidase, highly expressed by all prostate cancers and its expression increases with tumor aggressiveness, metastatic disease and disease recurrence [11-13]. PSMA is also expressed in small intestine, renal tubules, salivary glands and tumor neovasculature [14]. PSMA is a type II membrane glycoprotein that has a short cytoplasmic tail, single intramembrane coil and a large extracellular part, which retains the enzymatic activity. Enzymatic activity of PSMA hydrolyzes the neuropeptide N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) that leads the production of glutamate and N-acetylaspartate. The amount of glutamate as a neurotransmitter is closely related with some neurologic diseases and many small molecule inhibitors of this enzymatic activity is developed based on phosphonates, thiols or ureas in order to treat some of neuropsychiatric diseases [15]. Binding of inhibitors or antibodies to the extracellular domain increases the internalization rate of PSMA, which constitutes the rational of targeting for the delivery of radionuclides into the PSMA expressing cells.
The unique expression profile of PSMA provides an excellent target for prostate cancer imaging and therapy [16,17]. During last several years a number of small molecule PSMA enzyme inhibitors were labeled with radionuclides like I-123, I-131, Tc-99m, Ga-68 and Lu- 177. Recently, Ga-68 labeled small molecule inhibitors Ga-68-DKFZ-11 (Glu-NH-CONH- Lys-(Ahx)-[Ga-68 (HBED-CC)] has been shown to be a novel radiotracer that show high cell uptake with prolonged cell surface retention resulted in a high tumor contrast. Relatively easy and efficient radiolabeling technique has led the compound to be a potential radiotracer that may detect prostate carcinoma relapses and metastasis by targeting the PSMA [17].
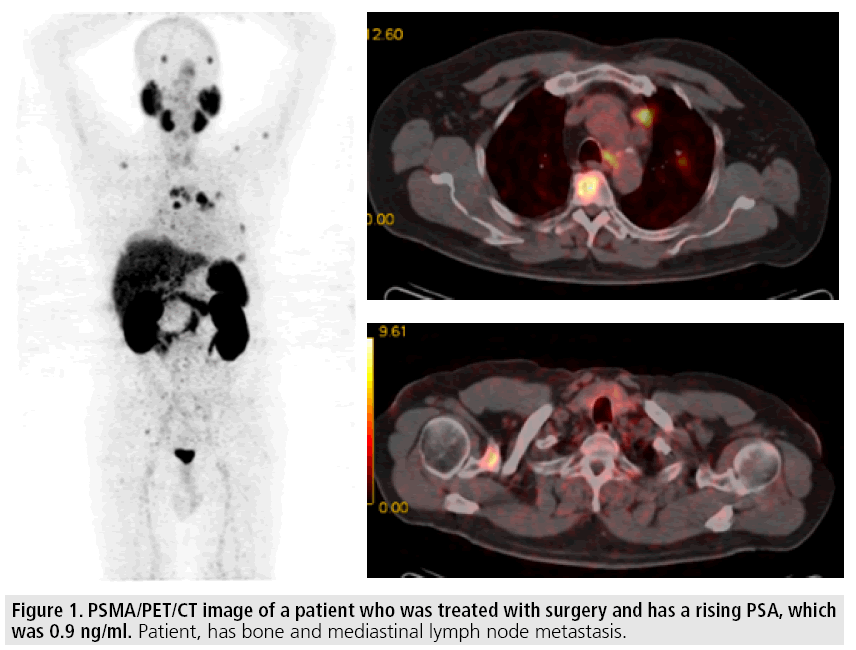
First human bio-distribution studies of PSMA PET/CT imaging have demonstrated intense radiotracer uptake in kidneys, salivary glands and urinary bladder due to excretion of radiotracer through kidneys [18,19] (FIGURE 1). High tracer uptake was observed at the sites of primary tumor, lymph and bone metastasis giving highest uptake at the sites of higher Gleason score. Afshar-Oromich et al. compared the positivity rate of PSMA PET/CT and F-18- choline PET/CT in 38 patients who have a suspicion of recurrence [20]. The detection rate was significantly higher for PSMA PET/ CT as compared to that of F-18-Choline PET/ CT (86.5% vs. 70.3% respectively p<0.05). When they analyzed the patients with low PSA levels this difference was more prominent in favor of PSMA, which also gave higher SUV max values than F-18-Choline. Giesel et al. compared the detection rate of PSMA PET/ CT with 3D CT volumetric lymph node in patients with recurrent prostate cancer [21]. PSMA imaging was considered to be positive 31 lymph nodes in 7 patients and could be able to detect as small as 2.4 mm lymph nodes. On the other hand only 36% of these nodes were larger than 8 mm, which was a threshold for positivity in CT imaging. Afshar-Oromich et al. studied 42 patients and compared the positive lymph nodes in PSMA PET/CT with biopsy or surgery results and found out 100% specificity for pathological tracer uptake in lymph nodes [22]. The diagnostic sensitivity and specificity was found to be 76.6% and 100%, respectively. These findings are highly promising and it seems that PSMA imaging may have a potential role for the restaging of the disease. However, more prospective studies are needed in order to understand the exact role of PSMA imaging for staging purposes.
Figure 1: PSMA/PET/CT image of a patient who was treated with surgery and has a rising PSA, which was 0.9 ng/ml. Patient, has bone and mediastinal lymph node metastasis.
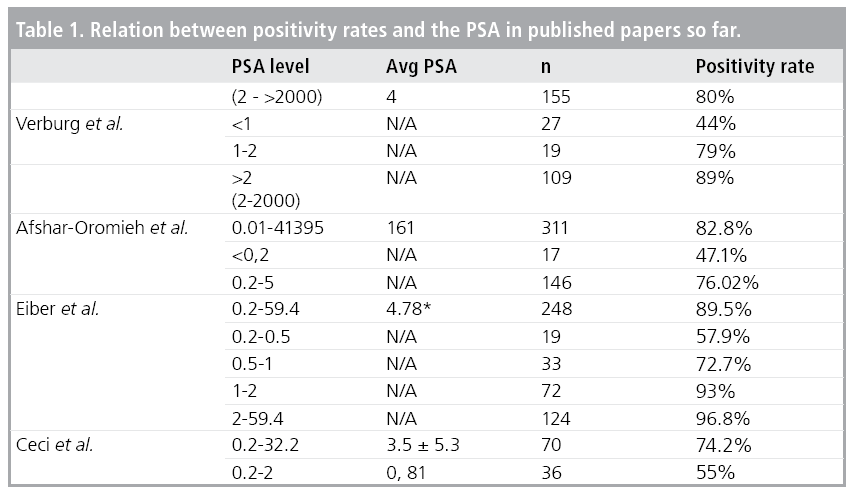
Afshar-Oromich et al. studied the diagnostic value of PSMA PET/CT in 318 patients with recurrent prostate cancer [22] (TABLE 1). The positivity rate was 82.2% in all-patient group. They reported high positive rates even in patients with low PSA values. The positivity rate was 47.1% and 64.3% in patients with PSA levels for <0.2 ng/ml and 0.2 to 2.0 ng/ ml respectively. They reported that positivity rate was positively associated with PSA level and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). Eiber et al. reported higher positivity rates in 258 patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy [23]. They found that the positivity rates are closely associated with PSA levels and PSA velocity but not PSA doubling time. They reported a 57.9% positivity rate in patients with low PSA values (<0.5 ng/ml), which may considerably influence the management of the disease. Ceci et al. [24] and Verburg et al. [25] have studied the factors that may have an impact on the detection rate of PSMA PET/CT in patients with recurrent prostate cancer. Ceci et al. have reported a positivity rate of 74.2% in 70 patients and in a ROC analysis they found a cut off value of 6.5 months for PSA doubling time and 0.83 ng/ml for PSA value. So patients with low PSA levels and longer PSA doubling time may have a less likelihood to have a positive scan. Verburg et al have reported a positivity rate of 44% in patients with PSA value of less than 1 ng/ml and they reported that positivity rate was positively associated with PSA level and PSA doubling time. Moreover, they showed these two parameters were independent determinants for finding M1 disease. These studies have shown that PET/CT imaging with a PCa targeted tracer, PSMA, seems to be a powerful tool and is superior to metabolic imaging radiopharmaceuticals like FDG and Choline. All these preliminary results suggest PSMA PET/CT can be used effectively for restaging purposes in order to develop a treatment strategy even in patients with low PSA levels but to be confirmed with prospective studies.
Unique expression of PSMA and high sensitivity of the Ga-68 labelled ligands also provides as an excellent target for its counterpart Lu-177-PSMA-617 as a tool for radionuclide therapy in castration resistant prostate cancer. Cases who have benefit from this type of therapy have already reported [26]. It has been shown that parotid glands and kidneys are the target organs for toxicity [27]. However, dosimetry studies have shown that Lu-177-PSMA therapy is a safe method and cumulative activity of up to 30GBq can be given using kidneys as dose limiting organ. Currently many centers are applying Lu-177-PSMA therapy and we eagerly waiting for the clinical results.
In conclusion, PSMA PET/CT seems to be a highly accurate imaging tool for restaging of prostate cancer patients with biochemical recurrence. For accurate management of patients who developed biochemical recurrence, It is extremely important to differentiate local disease from systemic in order to develop a treatment strategy and to decide if the patient is a candidate for a salvage therapy or not. The sensitivity of anatomic imaging techniques like CT scan or MR imaging and the metabolic imaging techniques like bone scan, FDG PET/CT, F-18 NAF PET/ CT or C-11 or F-18 labelled choline PET/CT imaging are far below then desired. PSMA PET/ CT imaging may be used in order to develop a treatment strategy even in patients with low PSA levels. As a theranostic approach its counterpart Lu-177 labelled ligands have a potential for the treatment of castration resistant prostate cancer.
References
- Brawley OW. Prostate cancer epidemiology in the United States. World. J. Urol. 30, 195-200 (2012).
- Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent-update 2013. Eur. Urol. 65, 124-137 (2014).
- Heidenreich A, Bastian BJ, Bellmunt J et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of advanced, relapsing and castration resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 65, 467-79 (2014).
- Briganti A, Abdollah F, Nini A et al. Performance characteristics of computed tomography in detecting lymph node metastases in contemporary patients with prostate cancer treated with extended pelvic lymph node dissection. Eur. Urol. 61, 1132- 1138 (2012).
- Budiharto T, Joniau S, Lerut E et al. Prospective evaluation of C-11-Choline positron emission tomography/computed tomography and diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the nodal staging of prostate cancer with a high risk lymph node metastases. Eur. Urol. 60, 125-130 (2011).
- Gakis G, Boorjian SA, Briganti A et al. The role of radical prostatectomy and lymph node dissection in lymph node positive prostate cancer: A systematic review of the literatüre. Eur. Urol. 22, S0302-2838 (2013).
- Heck MM, Souvatzoglou M, Retz M et al. Prospective comparison of computed tomography, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging and C-11-choline positron emission tomography/computed tomography for preoperative lymph node staging in prostate cancer patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 41, 694-701 (2014).
- Briganti A, Joniau S, Gandaglia G et al. Patterns and predictors of early biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy and adjuvant radiation therapy in men with pT3N0 prostate cancer: implications for multimodal therapies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 87, 960-967 (2013).
- Panebianco V, Barchetti F, Sciarra A et al. Prostate cancer recurrence after radical prostatectomy: The role of 3-T diffusion imaging in multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. 23, 1745-52 (2013).
- Ceci F, Castellucci P, Graziani T et al. 11C-choline PET/CT detects the site of relapse in the majority of prostate cancer patients showing biochemical recurrence after EBRT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 41, 878-886 (2014).
- Wright GL Jr, Haley C, Beckett ML et al. Expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen in normal, benign, and malignant prostate tissues. Urol. Oncol. 1, 18-28 (1995).
- Perner S, Hofer MD, Kim R et al. Prostatespecific membrane antigen expression as a predictor of prostate cancer progression. Hum. Pathol. 38, 696-701 (2007).
- Wright GL Jr, Grob BM, Haley C et al. Upregulation of prostate-specific membrane antigen after androgen-deprivation therapy. Urology. 48, 326-334 (1996).
- Silver DA, Pellicer I, Fair WR et al. Prostatespecific membrane antigen expression in normal and malignant human tissues. Clin. Cancer. Res. 3, 81-85 (1997).
- Bařinka C, Rojas C, Slusher B et al. Glutamate carboxypeptidase II in diagnosis and treatment of neurologic disorders and prostate cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 19, 856-870 (2012).
- Eder M, Schäfer M, Bauder-Wüst U et al. 68Ga-complex lipophilicity and the targeting property of a urea-based PSMA inhibitor for PET imaging. Bioconjug. Chem. 23, 688-697 (2012).
- Eder M, Schafer M, Bauder-Würst U et al. Preclinical evaluation of a bispecific lowmolecular heterodimer targetting both PSMA and GRPR for improved imaging and therapy of prostate cancer. Prostate. 74, 659-668 (2014).
- Afshar-Oromieh A, Malcher A, Eder M et al. PET imaging with a (Ga-68) gallium-labelled PSMA ligand for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: biodistribution in humans and first evaluation of tumour lesions. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 40, 486-495 (2013).
- Kabasakal L, Demirci E, Ocak M et al. Evaluation of PSMA PET/CT imaging using a 68Ga-HBED-CC ligand in patients with prostate cancer and the value of early pelvic imaging. Nucl. Med. Commun. 36, 582-587 (2015).
- Afshar-Oromieh A, Zechmann CM, Malcher A et al. Comparison of PET imaging with a (68) Ga-labelled PSMA ligand and (18)F-cholinebased PET/CT for the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 41, 11-20 (2014).
- Giesel FL, Fiedler H, Stefanova M et al. PSMA PET/CT with Glu-urea-Lys-(Ahx)-[(68) Ga(HBED-CC)] versus 3D CT volumetric lymph node assessment in recurrent prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 42, 1794-1800 (2015).
- Afshar-Oromieh A, Avtzi E, Giesel FL et al. The diagnostic value of PET/CT imaging with the (68)Ga-labelled PSMA ligand HBED-CC in the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 42, 197-209 (2015).
- Eiber M, Maurer T, Souvatzoglou M et al. Evaluation of Hybrid Ga-PSMA Ligand PET/CT in 248 Patients with Biochemical Recurrence After Radical Prostatectomy. J. Nucl. Med. 56, 668-674 (2015).
- Ceci F, Uprimny C, Nilica B et al. Ga-PSMA PET/CT for restaging recurrent prostate cancer: which factors are associated with PET/ CT detection rate? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 42, 1284-1294 (2015).
- Verburg FA, Pfister D, Heidenreich A et al. Extent of disease in recurrent prostate cancer determined by [68Ga]PSMA-HBED-CC PET/ CT in relation to PSA levels, PSA doubling time and Gleason score. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. (2015).
- Kratochwil C, Giesel FL, Eder M et al. Lutetium-labelled PSMA ligand-induced remission in a patient with metastatic prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 42, 987-988 (2015).
- Kabasakal L, AbuQbeitah M, Aygün A et al. Pre-therapeutic dosimetry of normal organs and tissues of Lu-177-PSMA 617 prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) inhibitör in patients with castration resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 42, 1976-1983 (2015).