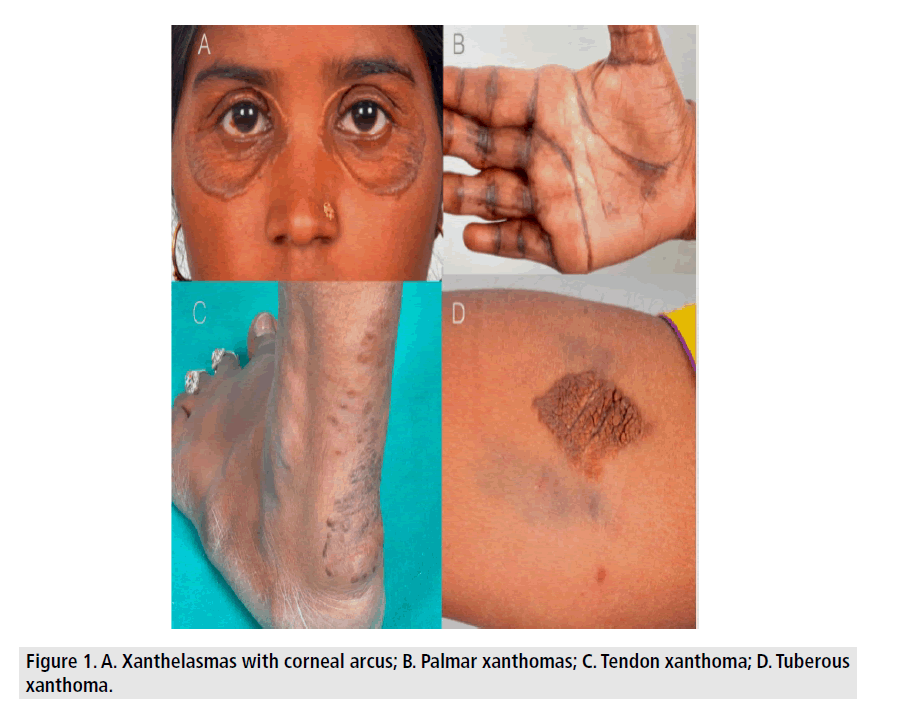
Clinical images - Imaging in Medicine (2017) Volume 9, Issue 5
Xanthomas in familial hypercholesterolemia
Laxman Ram Jhuria*, Sanjay Jain and Rajiv Ranjan KumarPost Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research,India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Laxman Ram Jhuria
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research
India
E-mail: laxmanjhuria91@gmail.com
Abstract
Keywords
xanthomas ▪ familial hypercholesterolemia
A 23 year lady was being evaluated for dyspnea on exertion and multiple episode of presyncope for 1 year. Incidentally she was found to have yellowish Xanthomatous skin lesion in multiple location and hyper pigmentation of palmar creases (FIGURE 1). Further enquiry revealed she is having these skin lesions since 6 years and her parents had similar skin lesions since childhood, who suffered sudden death at young age. Investigation showed raised serum total cholesterol (18.52 mmol/dl) and LDL-c (16.91 mmol/dl) with normal TG, HDL-c level and severe aortic stenosis on Echocardiography. Diagnosis of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia was considered and she was started on high intensity statin therapy (tab. Atorvastatin 80 mg/day) with aspirin and planned for cardiac catheterization followed by aortic valve replacement, but unfortunately she succumbed to sudden cardiac death at home. Familial hypercholesterolemia is a risk factor for premature atherosclerosis and subsequently coronary artery disease at younger age. Adequate health awareness and genetic counseling are needed for identification of these individuals at risk for sudden death and further prevention from spreading to the next generation.